Meaningful Innovation
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is an immune-mediated inflammatory condition that occurs in as much as 1% of the U.S. population.
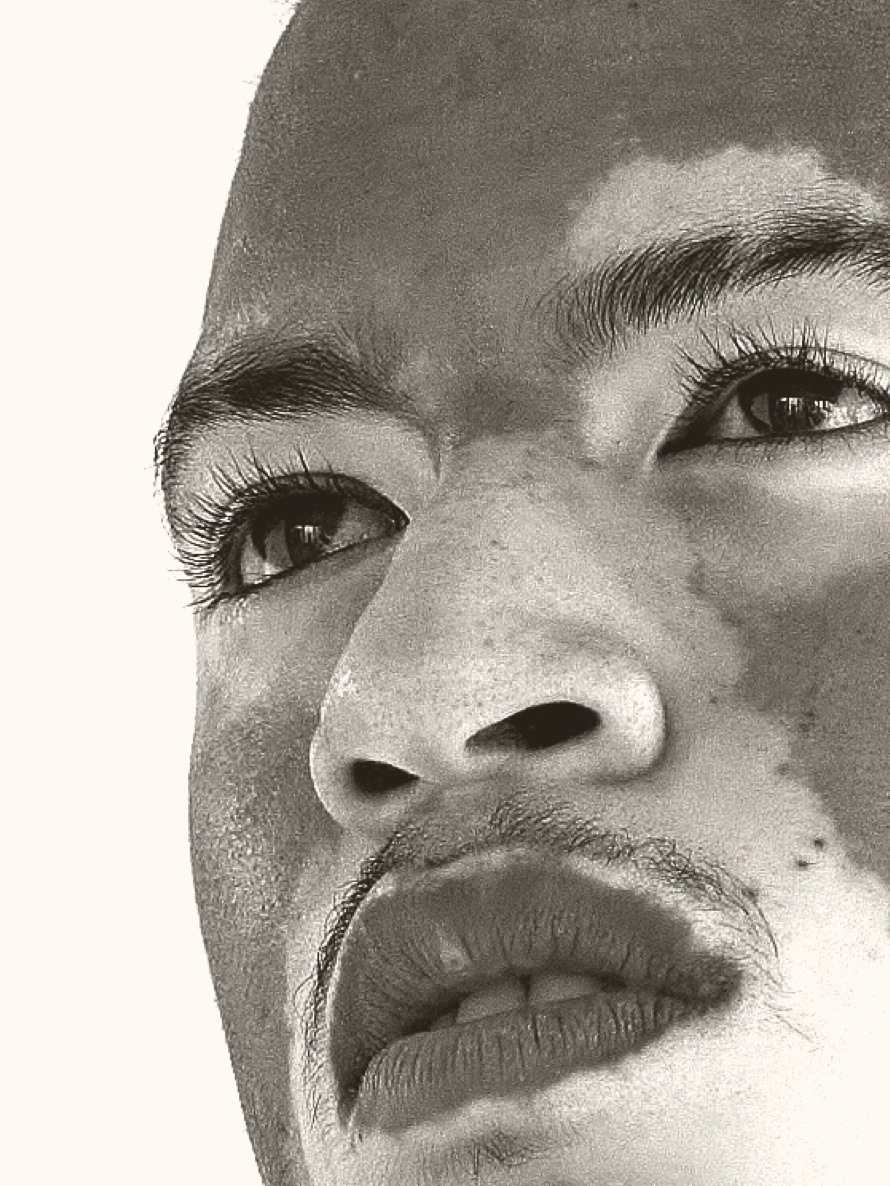
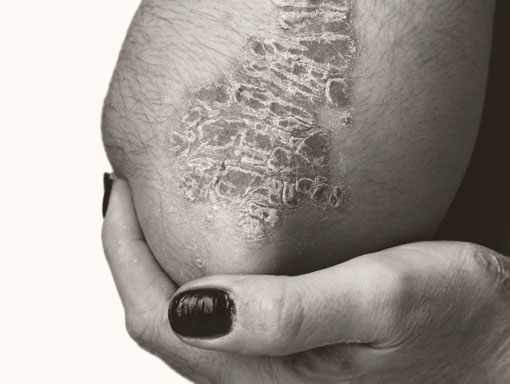
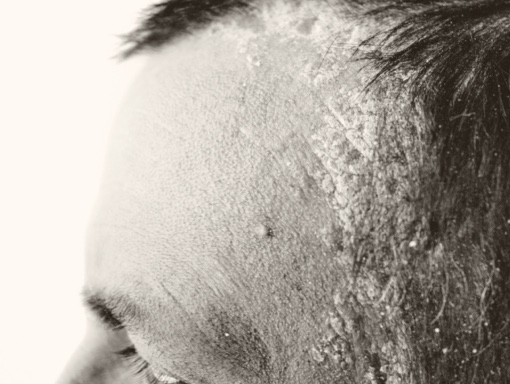
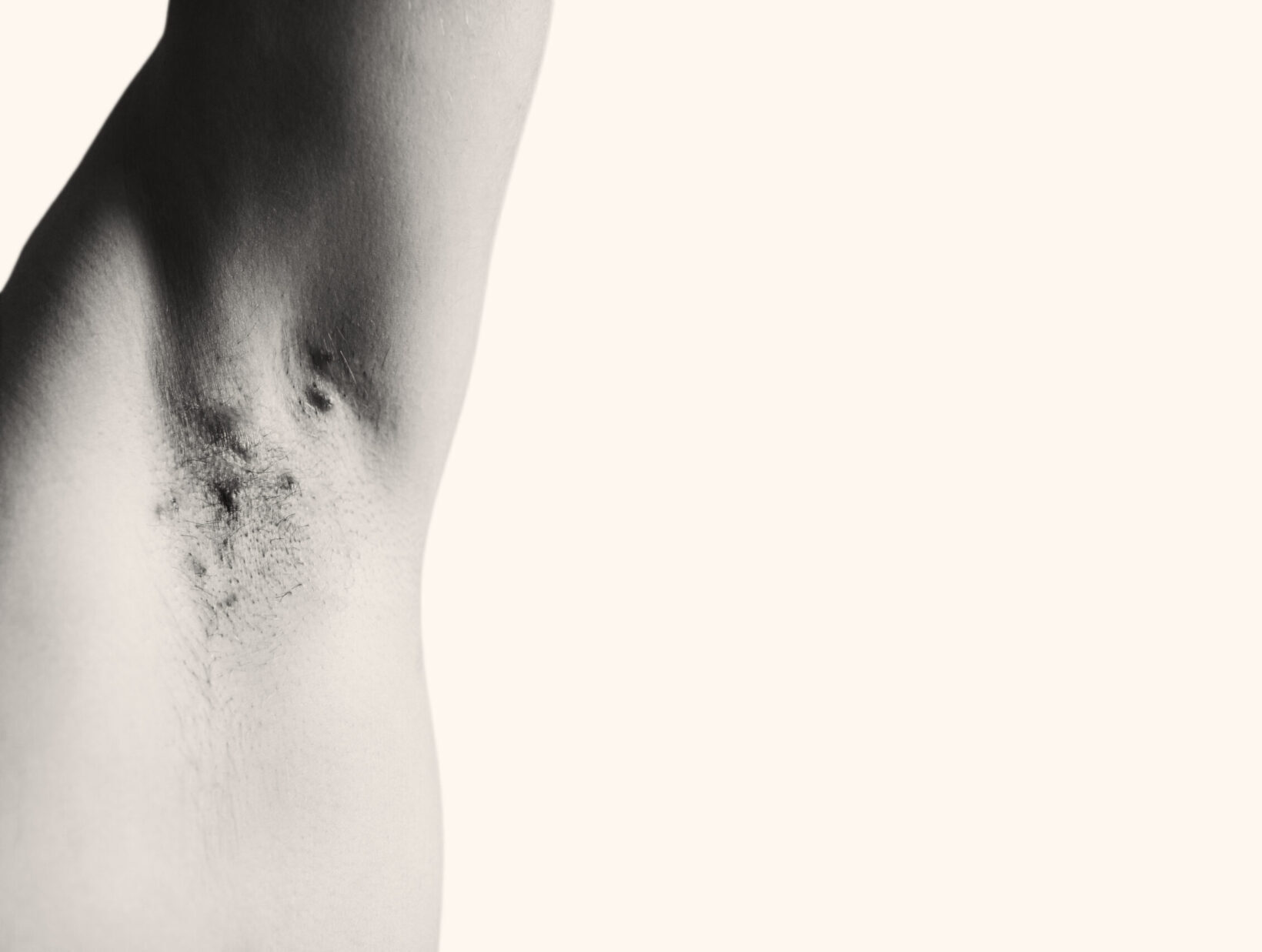
It is characterized by the loss of natural skin color (pigment) or by discolored patches on various parts of the body, including the face, neck, and scalp, as well as mucous membranes, including lips, resulting in white or light-colored areas.
Vitiligo is a multifactorial disorder of the skin in which the body’s immune system damages and destroys pigment-producing cells (melanocytes), the cells responsible for melanin production, resulting in loss of skin pigmentation.
Loss of pigmentation often starts on the hands, feet, or face and is typically progressive. It is a skin disease that affects people of all skin types but may be more noticeable in people with darker skin.
There are several types of vitiligo based on the pattern and distribution of de-pigmented patches. Non-segmental (also called generalized) is the most common type, and has a mirrored pattern, meaning it presents symmetrically on both sides of the body – such as both sides of the face, both hands, or both feet. Whereas segmental vitiligo typically presents at an early age, appearing on only one side of the body and in an isolated segment such as the leg, arm, or face.
Because of the effect on the person’s appearance, vitiligo can be life-altering and can have a substantial negative impact on the psychological well-being of patients and reduce quality of life. Vitiligo can lead to a poor body image, causing individuals to feel embarrassed or anxious about their skin and withdraw from social activities.
There are few FDA-approved treatments for vitiligo. As such there is a significant unmet need for patients who have vitiligo.
Explore our focus areas.
Broad and deep dermatology pipeline.
Learn about Arcutis’ current clinical programs.
View Pipeline